Smart speakers have rapidly become fixtures in homes worldwide. They offer hands-free convenience for everything from playing music to managing smart home devices. But what enables these devices to understand and respond to human speech so effectively? The answer is use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in smart speakers.
Machine Learning in Smart Speakers: Understanding the Basics
At their core, smart speakers such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri rely on AI technologies. Particularly natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning. This allows them to interpret and act on voice commands. The systems are designed to simulate human intelligence by recognizing patterns.
From Data to Understanding
The journey of a voice command through a smart speaker involves several steps
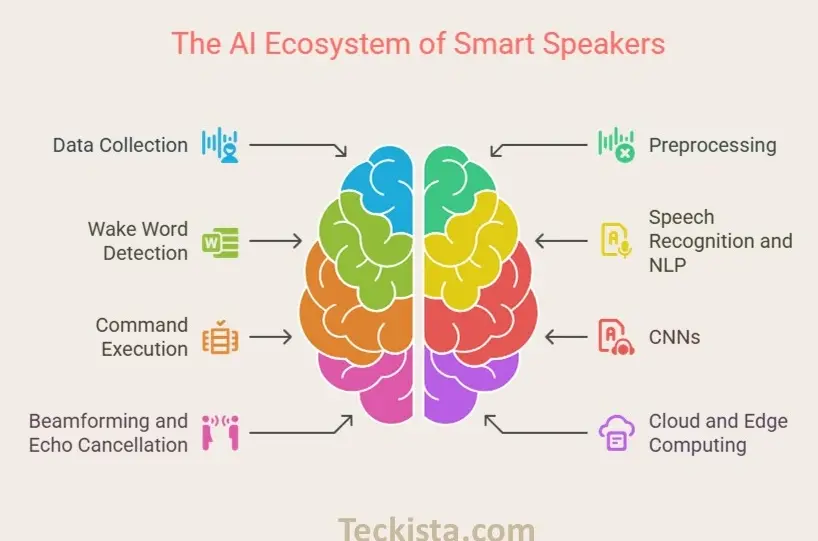
- Data Collection: Smart speakers are trained on vast datasets comprising audio samples from diverse accents, languages, and environments. This diversity ensures that the devices can understand a wide range of voices and speech patterns.
- Preprocessing: The raw audio input is processed to filter out background noise. Advanced algorithms help the device focus on the user’s voice, even in noisy settings.
- Wake Word Detection: The speaker continuously listens for a “wake word” like “Alexa” or “Hey Google.” Using specialized models based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). This process is optimized for both sensitivity and specificity, ensuring the device responds accurately without false triggers.
- Speech Recognition and NLP: Once activated, the device converts speech to text using automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. Machine learning models then analyze the text to determine the user’s intent.
- Command Execution: The interpreted command is executed. whether it’s playing a song, answering a question, or controlling a smart device. Importantly, the system learns from each interaction, improving its accuracy and responsiveness over time.
Key Technologies Powering Smart Speakers
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): CNNs are effective for audio recognition tasks. They extract features from audio signals, enabling the system to distinguish between different commands, accents, and even background noises.
- Beamforming and Echo Cancellation: Multiple microphones and beamforming algorithms help the device isolate the user’s voice from ambient noise, enhancing recognition accuracy.
- Cloud and Edge Computing: While some processing occurs locally on the device for speed and privacy, more complex tasks are often sent to the cloud, where powerful servers run advanced AI models and continuously update the speaker’s capabilities.
Check out the complete list of Top Alexa Enabled Speakers
Learning from Real-World Use
Smart speakers don’t just rely on their initial training. They continuously collect data from real-world interactions, allowing their machine learning models to adapt to new accents, languages, and usage patterns. User corrections and feedback are also incorporated. It makes the system smarter and more personalized over time.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
While the learning capabilities of smart speakers offer immense convenience. They also raise important privacy concerns. User interactions are often stored and analyzed to improve services. Which can lead to targeted advertising and data sharing with third parties. Transparency and user control over data are critical issues as these technologies evolve
More Human-like Interactions
As machine learning and AI continue to advance, smart speakers are expected to become even more proactive and intuitive. Future devices may offer personalized recommendations in a more human-like manner, further blurring the line between technology and daily life.
